Radiofrequency ablation for Barrett’s esophagus
Description
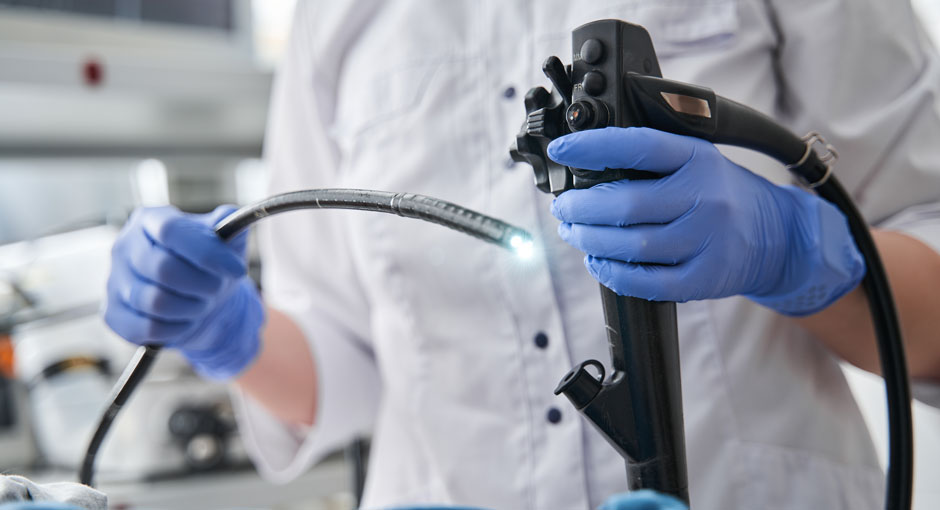
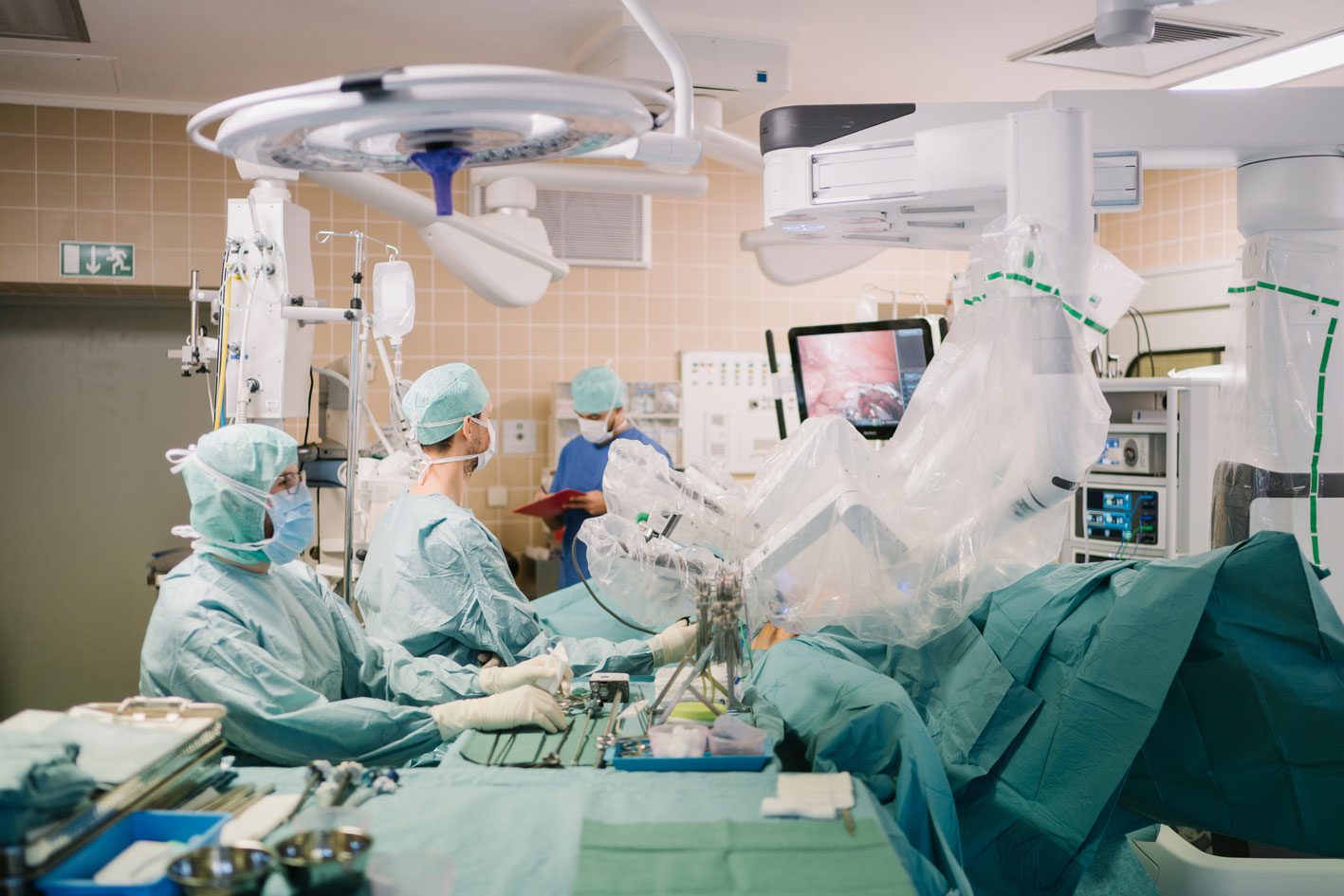
Barrett’s esophagus is the main risk factor for esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC, with a 50-fold increased risk). Removing the Barrett’s mucosa significantly reduces this risk. If neoplastic areas of Barrett’s esophagus (i.e., cells that have the potential to become malignant or have already done so) have been previously resected by endoscopy. It is recommended, according to current reflux guidelines, to treat/remove the remaining Barrett’s mucosa (even if it is non-dysplastic). A safe and gentle method is radiofrequency ablation (RFA), which involves removing the precancerous mucosa damaged by Barrett’s esophagus through gastroscopy (gastric endoscopy) under sedation during an outpatient procedure, while preserving the underlying healthy tissue.
The endoscopic procedure lasts approximately 30 to 45 minutes, and patients can generally leave the clinic the same day. In case of occasional mild discomfort, we provide medication to the patients. After 2 to 3 months of treatment, a follow-up gastroscopy is performed to determine if an additional RFA session is necessary.
Added value
Thanks to the technology of the Barrx radiofrequency ablation system offered by its gastroenterology department, the Robert Schuman Hospitals are the only center in Luxembourg capable of treating patients with Barrett’s esophagus requiring treatment at the Zithaklinik, thus reducing the relative risk of disease progression from low-grade dysplasia to high-grade dysplasia or EAC by up to 94%.
Status
Fully operational since June 2021.

Photo gallery